Soldering is a common technique used in many different fields, including electronics, jewelry making, and metalworking. While soldering can be a simple and effective way to join two metal surfaces, many common problems and mistakes can occur during the soldering process. These problems and mistakes can range from the formation of "cold joints" to the formation of dross or tinning on the surface of the metal. To avoid these problems and create strong, reliable soldered joints, it is important to understand the most common problems and mistakes that can happen with soldering and to take steps to prevent or correct them.
Insufficient heat: For the soldering material to properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces, it must be heated to a high enough temperature to melt and flow. If the temperature is too low, the soldering material will not be properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces, resulting in a cold joint. This can be caused by using a soldering iron or soldering torch that is not hot enough or by applying heat for too short a time.
Improper cleaning of the metal surfaces: For the soldering material to properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces, it must be free from dirt, grease, and other contaminants. If the metal surfaces are not properly cleaned before soldering, the soldering material may not be properly wet, and bond with them, and a cold joint will result. This can be avoided by thoroughly cleaning the metal surfaces with a solvent or other cleaning solution before soldering.
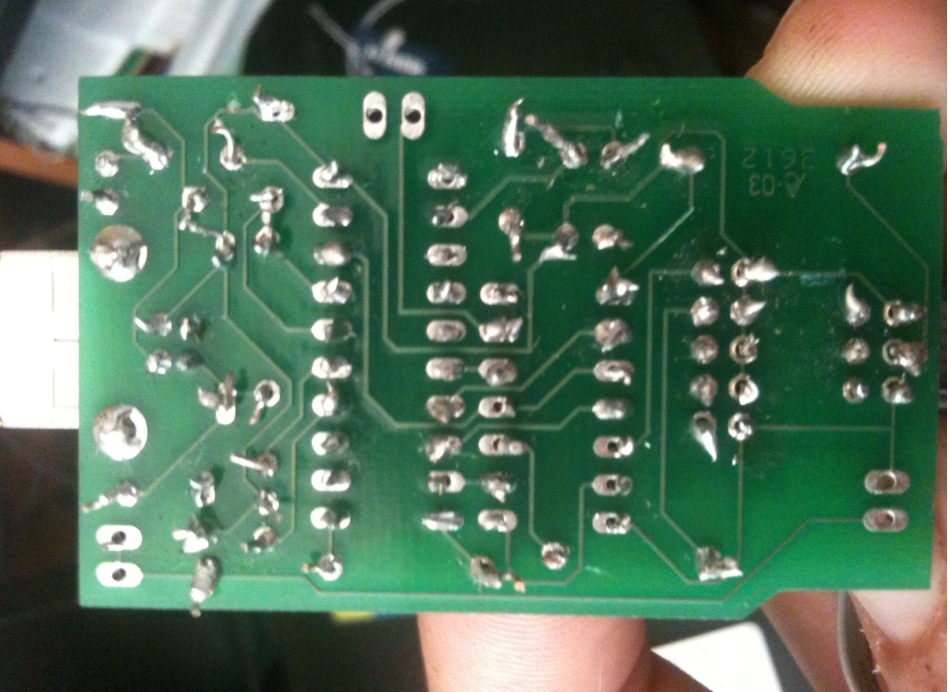
Use a soldering iron or soldering torch that is not hot enough: For the soldering material to properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces, the soldering iron or soldering torch must be hot enough to melt and flow the soldering material. If the soldering iron or soldering torch is not hot enough, the soldering material may not be properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces and a cold joint will result. This can be avoided by using a soldering iron or soldering torch appropriate for the type and size of metal surfaces being soldered.
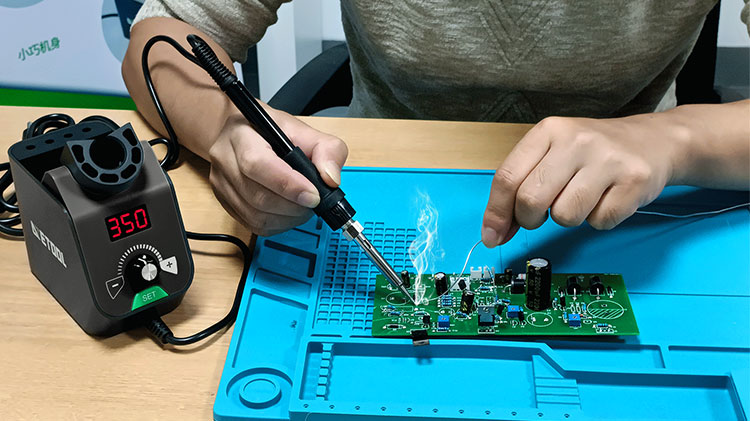
Use of a soldering material that is not suitable for the application: Different soldering materials have different melting points, flow characteristics, and other properties that make them suitable for different applications. If the wrong soldering material is used, it may not get properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces and a cold joint will result. This can be avoided by carefully selecting the right soldering material for the application.
Presence of impurities in the soldering material: The soldering material must be free from impurities in order for it to properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces. If the soldering material contains impurities such as oxides or other contaminants, it may not get properly wet and bond with the metal surfaces and a cold joint will result. This can be avoided by using high-quality soldering material and properly storing and handling it to prevent contamination.
Use a soldering iron or soldering torch that is not properly maintained or calibrated: For the soldering iron or soldering torch to provide the right amount of heat and flow the soldering material properly, it must be properly maintained and calibrated. If the soldering iron or soldering torch is not properly maintained or calibrated, it may not provide the right amount of heat, and a cold joint will result. This can be avoided by regularly cleaning, maintaining, and calibrating the soldering iron or soldering torch.
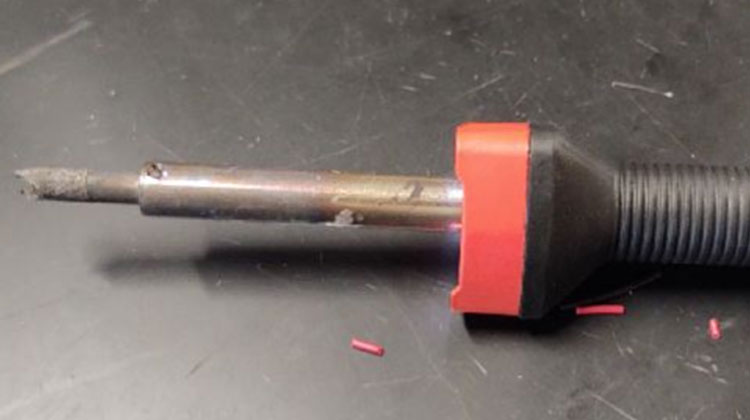

Excessive heat: If the soldering iron or soldering torch is too hot, or if heat is applied for too long, it can cause the metal surfaces to become discolored, distorted, or even melted. It can also cause the soldering material to become brittle and crack, compromising the soldered joint's strength and reliability. This can be avoided by carefully controlling the temperature, time, and amount of heat used during the soldering process.
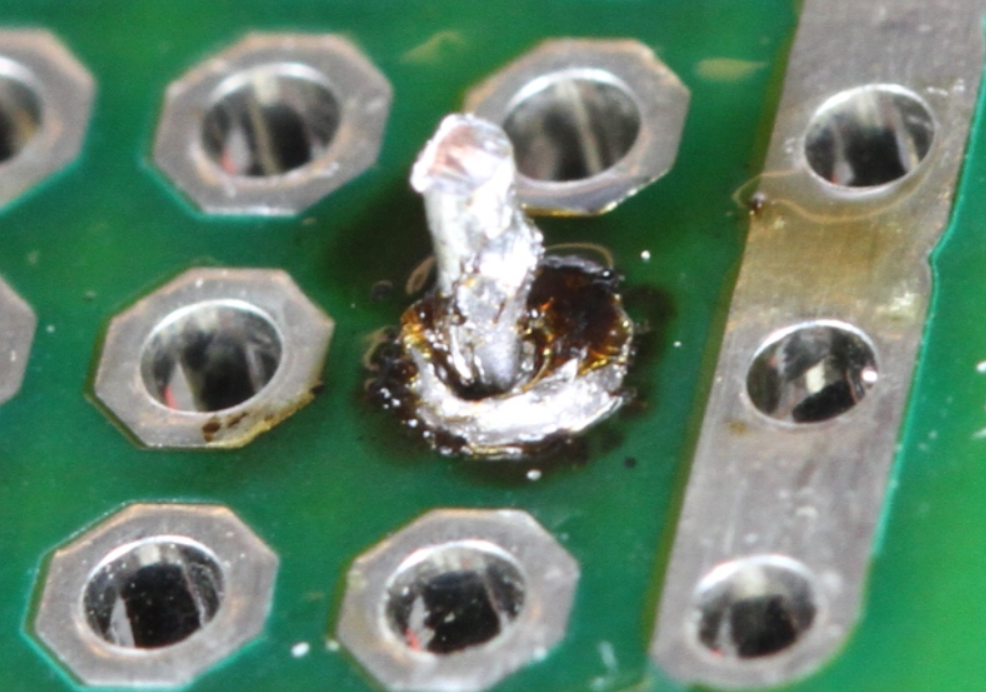
Formation of dross: Excessive heat can cause the soldering material to form "dross" on the surface of the metal. Dross is a type of oxide or other impurities that can form on the surface of the metal as a result of overheating.
Formation of tinning: Tinning occurs when the soldering material adheres to the surface of the metal in a thin, even layer. While tinning can provide some benefits, such as improving the wetting and bonding of the soldering material, it can also be detrimental if done excessively. Excessive tinning can cause the soldering material to build up in thick layers, creating a messy and uneven joint. It can also cause the soldering material to become brittle and crack, compromising the soldered joint's strength and reliability.
To avoid these problems and mistakes, it is important to carefully control the temperature, time, and amount of heat and soldering material used during the soldering process. This can help to ensure that the soldered joint is strong, reliable, and free from defects or failures. Additionally, using the right tools and equipment for the job and maintaining a safe and organized workspace while soldering is important. By following these guidelines, you can avoid common problems and mistakes with soldering and create strong, reliable soldered joints.
Contact: Mr. Li
Phone: (0086) 138 24254 321
E-mail: atetool@atetool.com.cn
Add: 5F, 1-2# Building, Tongfuyu Industrial Zone, Aiqun Rd, Shiyan Subdistrict, Bao'an, Shenzhen, 518108, China